Every drug prescribed
Every over-the-counter drug added…
…brings the potential for costly ADRs.
Globally, preventable medication errors cost over $1 trillion each year.
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) are among the leading causes of additional complications and longer hospital stays, morbidity and mortality.
It has been estimated that ADRs are the 4th largest cause for mortality in the USA, resulting in the deaths of several thousands of patients each year.
Click here to read more about the devastating effects of ADRs both to patients and to healthcare providers>>
Click here to contact us now by email or schedule a call
Quantum Satis
Turning the tide on ADRs
The power of QS AI
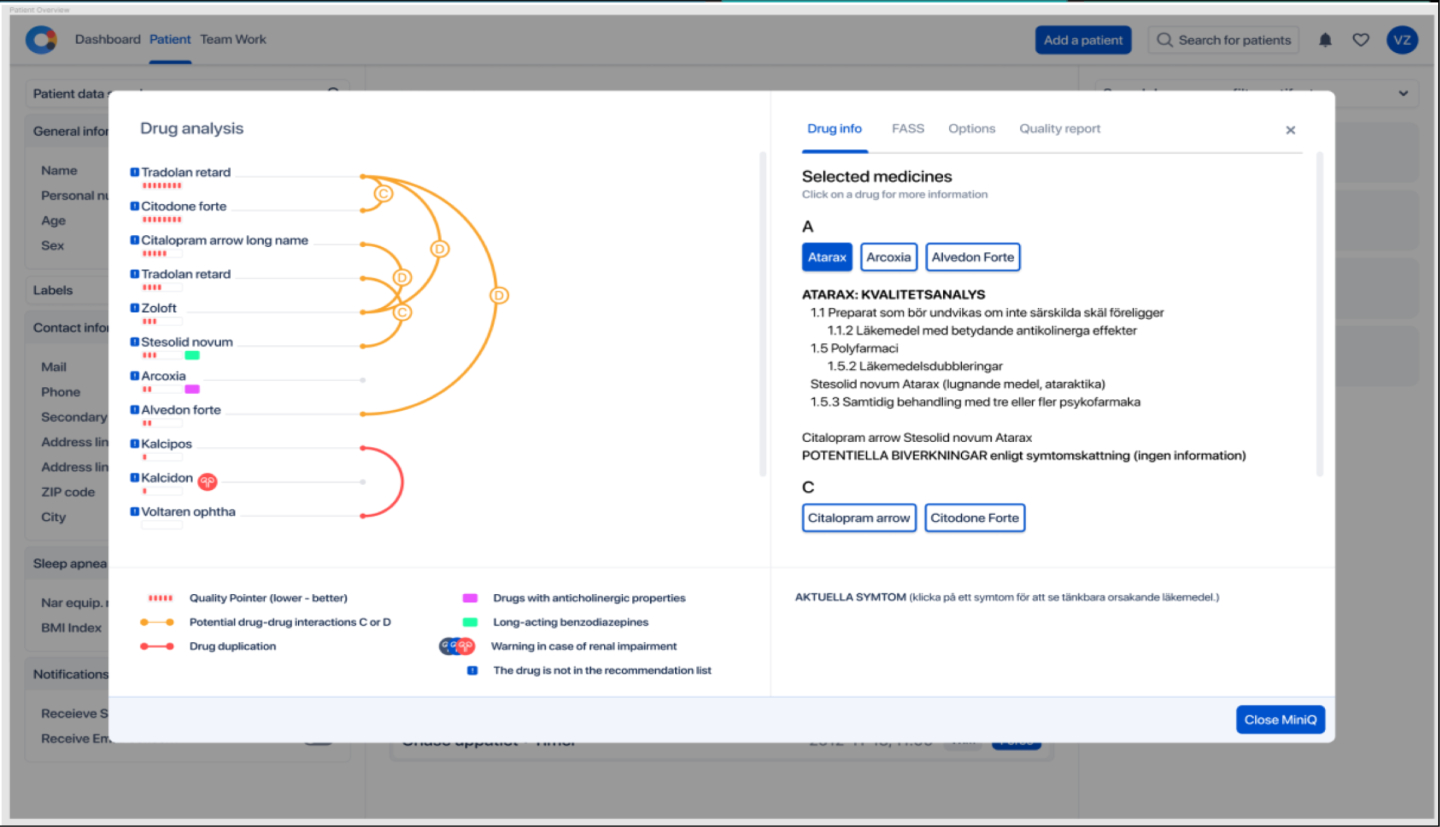
Quantum Satis is a powerful AI-based medical evaluation tool which supports prescribing at the point of delivery. It reveals potential drug combination issues regardless of the complexity of the proposed or existing drug regime of that patient. It can reveal drug specific indicators (such as inappropriate drugs, drug duplication, drug-drug interactions etc) and diagnosis specific indicators (drug-disease interactions, contraindications etc).
It can quickly identify, collate and present its analysis in a clear and intuitive format. It interrogates the relevant drug combination data from across multiple datasets and combines that with an individual’s health history, physiology and symptoms to provide a tailored response.
Please contact me
The massive Adverse Drug Reaction problem encountered globally by healthcare organisations
Annual rise in hospital admissions due to ADRs
%
United Kingdom
%
France
%
Norway
Globally, preventable medication errors cost over $1 trillion each year, of which the U.S. economy alone incurs $21 billion.
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) are among the leading causes of additional complications and longer hospital stays, morbidity and mortality.
It has been estimated that ADRs are the 4th largest cause for mortality in the USA, resulting in the deaths of several thousands of patients each year. National USA Vital Statistics System data showed that from 1999 to 2006, the rate of ADR-related deaths increased from 0.08 to 0.12 per 100,000 persons.
It is estimated that up to 70% of ADRs leading to emergency department visits are preventable, with some countries spending up to 15-20% of their healthcare budgets treating otherwise avoidable ADRs.
The strain that ADRs place on the health care system is significant yet preventable.